Content of the Article
Psoriasis, scientifically known as psoriasis, is an autoimmune disease that causes rapid accumulation of skin cells. The accumulation of cells causes sores in the form of clusters on the skin surface. There is widespread inflammation and redness around the wounds. The typical mother-of-pearl appearance is white-silver with thick red patches developing. Sometimes these sores crack and bleed.

What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is an autoimmune skin disorder that causes skin cells to multiply several times faster than normal. In autoimmune diseases, the immune system is very active. The body attacks and damages its own tissues.
Psoriasis is the result of an accelerated skin production process. In the normal production process, skin cells deepen in the skin and slowly rise to the surface. They eventually fall. The typical life cycle of a skin cell is 1 month. In people with psoriasis, this production process takes place in just a few days. Therefore, the skin cells do not have time to fall off. This rapid overproduction leads to the accumulation of skin cells.
Lesions typically develop at joints such as the elbows and knees. It can also develop anywhere on the body, such as the hands, feet, neck, scalp, face. In the less common type of psoriasis, symptoms of the disease are also seen around the nails, mouth and genitals.
What Causes Psoriasis?
In psoriasis, various antigens are created by cells in the skin. These antigens play a role in activating the immune system. Active immune cells return to the skin and cause cell proliferation and the formation of disease-specific plaques in the skin.
Over the years, it has been determined that the disease is based on two causes, namely the immune system and genetics.
- Immune system
Psoriasis an autoimmune diseasetruck. This disease occurs when white blood cells known as T cells mistakenly attack skin cells.
Normally, white blood cells are tasked with fighting bacteria attack and infection. The accidental attack causes the skin cell production process to become over-accelerated. Accelerated skin cell production allows skin cells to develop rapidly, and they are pushed to the skin surface and piled on the skin.
This causes blemishes, which is the most common symptom of psoriasis. Attacks on skin cells cause red, raised areas to form on the skin surface.
- Genetic
Some people carry genes that put them at risk of developing psoriasis. If a family member has psoriasis or another skin condition, they are at higher risk of developing the disease. The rate of contracting the disease by genetic means is as low as 2% or 3%.
Psoriasis Symptoms
- Mother-of-pearl flaking and crusting, especially in the knees and elbows. These skin lesions can also be observed in the genital area, nails and scalp. There are also gray-white skin rashes and crusting on the arms, legs, palms and soles of the feet with red spots.
- Holes in the nails, thickening, yellow color formation, swelling and redness around the nails
- Dry skin, burning sensation, itching and bleeding
- Pain, swelling and redness in the joints
- Pain around the spots
Psoriasis symptoms often vary from person to person and depend on the type of psoriasis.
Some people with psoriasis may experience symptoms. Severe symptoms appear for a few days or weeks. It then disappears almost completely or is not noticeable at all. The disease flares up when a triggering situation occurs. Sometimes it disappears completely. That is, the disease remains in remission. Its disappearance does not mean that the disease will not flare up.

Types of Psoriasis
Psoriasis occurs in five different forms: plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
- Plaque psoriasis (Plaque psoriasis)
This type is the most common type of psoriasis. Plaque-type psoriasis accounts for 80% of psoriasis patients. It causes red, inflamed lesions that cover the skin. These lesions are mostly covered with white-silver scales and plaques. These plaques form on the elbows, knees, and scalp.
- Guttate psoriasis
Guttate psoriasis is common in childhood. This type of psoriasis causes small pink patches and is about the size of a coin. Common sites of guttate psoriasis are the trunk, arms, and legs.
- Pustular psoriasis
Pustular psoriasis is more common in adults. It causes white, pus-filled blisters and red, inflamed sores over large areas of skin. Pustular psoriasis usually appears on smaller areas of the body such as the hands or feet.
- Inverse psoriasis
This species has a red, shiny, inflamed appearance. Lesions develop in the armpits or breasts, in the groin or in the genital area, where the skin folds.
- Erythrodermic psoriasis
This type of psoriasis usually covers large parts of the body at once and is very rare. The skin looks almost like a sunburn. It's common for someone with this type of psoriasis to get a fever or get sick. The patient needs to be treated in an inpatient and hospital setting.
In addition to the types of psoriasis listed above, there is also the shape seen on the nails and scalp, which is named according to the area where it occurs.
Nail psoriasis
Nail involvement in psoriasis is quite common. Fingernails are more affected than toenails. The condition is often confused with fungal infections and other infections of the nail.
In this case, nail hole, grooves, discoloration, cracking or splitting of the nail, thickened skin under the nail and colored spots under the nail occur.
psoriasis in hair
Psoriasis It is manifested by plaques with sharp borders, red base and white dandruff on the scalp, which are located on the scalp.. Lesions are itchy. It can cause severe dandruff. It can extend to the neck, face, and ears and can be a large wound or smaller sores.
In some cases, it even complicates the care of the hair. Excessive scratching causes hair loss and scalp infections. This creates a source of social stress. Topical treatments are effective, requiring regular care, especially in the first two months.
Is psoriasis contagious?
Psoriasis is not contagious. That is, it does not pass from one person to another through the skin. Touching a psoriatic lesion by another person does not cause the condition to develop.

How Is Psoriasis Diagnosed?
Psoriasis is easily diagnosed during a physical examination when it is active. During the physical examination, the body is checked, especially the scalp, ears, elbows, knees, belly button and nails. If the symptoms are vague and the doctor does not want to leave any room for doubt, a small piece of skin is taken and a biopsy is requested. The skin sample is sent to the laboratory for examination under a microscope. As a result, psoriasis is diagnosed.
Causes of Psoriasis
The most well-known trigger of psoriasis is stress. Experiencing a higher-than-normal level of stress causes symptoms. Stress stands out as the most common trigger of psoriasis, as almost half of the patients struggle with chronic depression. Conditions that trigger psoriasis include:
- Stress
Experiencing an unusually high level of stress can lead to an exacerbation of the disease. The exacerbation of the disease will decrease if you learn to control and manage stress.
- Alcohol
Excessive and heavy alcohol consumption can cause psoriasis. The higher the frequency of alcohol consumption, the more frequent the psoriasis flare-ups will be.
- injuries
Having an accident, cutting yourself, or scraping your skin can trigger psoriasis. Skin injuries, vaccinations, sunburns can produce such effects on the skin.
- Medicines
Some medications can trigger psoriasis. These drugs are lithium, antimalarial drugs, and high blood pressure drugs.
- Infection
Psoriasis is caused in part by the immune system mistakenly attacking skin cells. When you are sick or fighting an infection, the immune system works too fast to fight the infection. This condition triggers psoriasis.
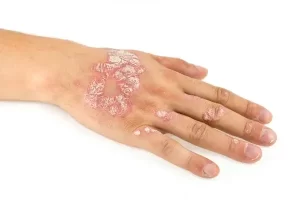
Psoriasis Treatment
Psoriasis treatment aims to reduce inflammation and flaking, slow the growth of skin cells, and lighten blemishes. Treatment of the disease falls into three categories: Topical treatments, systemic medications, and light therapy.
Topical treatments
Creams and ointments applied directly to the skin help treat mild to moderate psoriasis. The following are used in the treatment of psoriasis:
- Topical corticosteroids
- Topical retinoids
- Anthralin
- Vitamin D supplements
- Salicylic acid
- Humidifiers
Systemic drugs
People with moderate to severe psoriasis and those who do not respond well to other types of treatment should use oral or injected medications. Many of these drugs have serious side effects. This is why doctors usually prescribe it for short periods of time. Medications include:
- Methotrexate
- Cyclosporine
- Biologicals
- retinoids
Light therapy (phototherapy)
Ultraviolet (UV) or natural light is used in the treatment of psoriasis. Sunlight kills overactive white blood cells, which attack healthy skin cells and cause rapid cell proliferation. Both UVA and UVB light are effective in reducing mild to moderate psoriasis symptoms.
Most people with moderate to severe psoriasis benefit from a combination of treatments. This type of therapy uses more than one type of treatment to reduce symptoms. Some people continue treatment their entire life. They may need to change treatments occasionally if their skin doesn't respond to what they're using and other treatments.
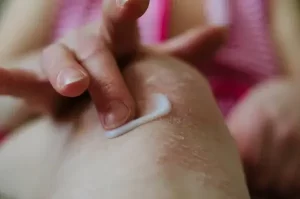
Drugs Used in Psoriasis
Cancer drugs such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, vitamin A forms known as retinoids and fumarate derivative drugs are among the systemic drugs used in the treatment of psoriasis. The most commonly used oral and injectable medications to treat psoriasis include:
- Biological drugs
These drugs alter the immune system. It inhibits the interaction between the immune system and related inflammatory pathways. These drugs are injected or given by intravenous infusion (administration of drugs or fluids into a vein through a tube system).
- retinoids
These drugs reduce skin cell production. Once you stop using them, the disease will likely return. Side effects include hair loss and lip inflammation. Women who are or may become pregnant within the next three years cannot use retinoids because of the possible risk of birth defects.
- Cyclosporine
This drug inhibits the immune system response, which relieves the symptoms of the disease. Side effects include kidney problems and high blood pressure.
- Methotrexate
Like cyclosporine, this drug suppresses the immune system. It produces fewer side effects when used in low doses. But in the long run, it can cause serious side effects. These include liver damage, decreased production of red and white blood cells.

Nutrition in Psoriasis
food It cannot cure psoriasis, but a healthy diet alleviates the course of the disease. How should psoriasis patients eat and what changes should they make in their lives? Let's list what you need to know about it.
Lose weight
- Losing weight reduces the severity of the disease. It also makes the treatment more effective.
Consume anti-inflammatory foods
A healthy diet changes the course of the disease. Since it is an autoimmune disease, foods that will improve the immune system and relieve inflammation should be consumed.
- Antioxidant-rich foods such as fresh fruits, vegetables, nuts and whole grain foods are recommended against psoriasis.
- Exposure to the sun at the right time with vegetables and fruits such as tomatoes, watermelons, carrots and melons, which are very rich in vitamins A and D, is one of the methods that should be applied for psoriasis.
- Zinc-rich foods such as milk, yoghurt and kefir, probiotic-rich foods, beef, legumes and seeds, high-fiber foods are very beneficial for the skin.
- Lean protein containing omega 3 fatty acids such as salmon, sardines and shrimp should be increased.
Stay away from alcohol
- Alcohol consumption causes exacerbation of the disease. Remove this item from your life.
be exposed to the sun
- Vitamin D Maintaining normal levels can be difficult without moderate sun exposure. In psoriasis, having vitamin D in the normal range is extremely important because it reduces cell production.
- Of course, you shouldn't be in the sun all day. It is good to get 20 minutes of sunlight preferably in the morning every day.
Keep your skin moist
- With psoriasis, there is dry, crusty, itchy, or inflamed skin that needs hydration. Almond oilCold pressed natural oils such as olive oil and avocado oil soften your skin and help maintain moisture levels.
- But dry skin can worsen with washing when harsh soaps and shampoos are used. Even hot water damages the skin affected by psoriasis. Therefore, you should take a bath with warm water.
Fish oil
- Fish oil is good for psoriasis. A moderate improvement is achieved.
gluten free diet
- In some studies, it is stated that a gluten-free diet is good for psoriasis.
Psoriatic Arthritis
In some psoriasis patients, the immune system attacks the joints as well as the skin, causing inflammation in the joint. This condition, called psoriasis rheumatism, is the name given to joint inflammation seen in approximately 15-20% of psoriasis patients.
This type of arthritis causes swelling, pain, and inflammation in the joints and affected joints. It is often confused with rheumatoid arthritis and gout. The presence of inflamed, red skin areas with plaque often distinguishes this type of arthritis from others.
Psoriatic arthritis is a chronic condition. Like psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis symptoms can flare up or stay in remission. This condition usually affects the joints of the lower body, including the knees and ankles.
Treatment of psoriatic arthritis successfully relieves symptoms and pain and improves joint mobility. As with psoriasis, losing weight, eating healthy, and avoiding triggers will reduce flare-ups. Early diagnosis and treatment reduces the likelihood of serious complications such as joint damage.

How Is Psoriasis Treated Naturally?
There is no definitive solution or treatment for psoriasis, which is not a life-threatening or contagious condition. Various topical steroids are used in the treatment. However, there are natural ways to alleviate the course of the disease. Although natural methods do not completely cure psoriasis, they improve the quality of life by reducing the symptoms.
What is good for psoriasis?
- Olive oil
- Rosehip oil
- Linseed oil
- Coconut oil
- Tea tree oil
- Fish oil
- Carbonate
- dead sea salt
- Turmeric
- Garlic
- Aloe vera
- Wheatgrass Juice
- Green tea
- saffron tea
- Ayran
Olive oil
- Apply olive oil to the wounds that develop on the skin. Reapply the oil every few hours.
Olive oil It acts as an emollient to moisturize the skin. Applying it regularly keeps skin supple, along with healing injured skin.
Rosehip oil
- Apply the rosehip oil on the affected area and leave it open. Apply it several times throughout the day.
Rosehip oil contains omega fatty acids, vitamins A and E, and antioxidants. These nourish the skin, relieve dryness and itching. It also heals damaged and inflamed cells.
Linseed oil
- Apply a few drops of flaxseed oil to the affected area and massage for a few minutes. Use this oil three to four times a day.
Linseed oilIt is a rich source of antioxidants such as alpha-linolenic acid (ALA), omega 3 fatty acids, tocopherol and beta carotene. It balances the pH value of the skin and moisturizes it. In this way, the effects of the disease are reduced.
Coconut oil
- Apply coconut oil liberally on your body, preferably after taking a bath. You can do this every day.
The anti-inflammatory properties of coconut oil relieve the pain associated with psoriasis. Its antibacterial properties keep the skin away from infection and provide moisturization with its softening properties.
Tea tree oil
- Mix 3-4 drops of tea tree oil with 1 tablespoon of olive oil and apply to the affected area.
- Apply this oil several times a day, especially if you suspect an infection.
Tea tree oil is useful in preventing infections that can occur in cracks caused by scratching the skin while scratching. Tea tree oil it also reduces inflammation.
Attention!!!
Do an allergy test before using tea tree oil. If it is not suitable for your skin type, it may cause the disease to worsen.
Fish oil
- Puncture the fish oil capsule to extract the oil contained in it.
- Apply directly to the skin.
- You can also take fish oil pills daily.
For psoriasis Fish oil It is very useful and a lot of work has been done on it. Omega 3 and omega 6 fatty acids in its content have an anti-inflammatory effect on the skin and relieve irritation. As a result of regular intake, it keeps the skin healthy and supple.
Carbonate
- Pour the warm water into the basin and add ⅓ cup of baking soda. Mix it well.
- Soak the affected areas in this water for about 15 minutes. Then wash with normal water.
- You can also add baking soda to a tub of water and soak in it.
- This practice, done daily for at least three weeks, will alleviate the symptoms of the disease.
Carbonate is slightly alkaline. It regulates the pH of the skin and increases the flow of electrolytes to the skin surface. It soothes the skin, reduces inflammation and also removes dead and dry skin cells.
dead sea salt
- Add 1 cup of dead sea salt to warm water and soak for 15 to 30 minutes.
- Then wash your body with clean water.
- You can do this every day.
Dead sea salt is enriched with minerals such as sodium, magnesium and bromide that act on and heal inflamed and irritated skin. It reduces dryness, moisturizes and softens the skin.
Vitamin D
- Psoriasis is caused by an overactive immune system. This overactivity can be regulated by the use of vitamin D. Vitamin D Containing foods and supplements can relieve the itching and discomfort caused by psoriasis.
- You can eat foods rich in vitamin D such as fish, eggs, dairy products.
- You can also take vitamin D supplements.
Vitamin E
- Vitamin E protects the skin from harmful UV rays. It also nourishes and keeps it soft. When not produced in sufficient quantities naturally by the body, it can cause psoriasis.
- A daily vitamin E supplement can be taken to compensate for this deficiency. Vitamin E oil can also be applied topically to relieve itching and reduce dryness.
Turmeric
- Add 2 teaspoon of powdered turmeric to 1 glasses of water. Cook for a few minutes on low heat. A thick paste will form.
- Leave the paste to cool. Apply to the affected area. Store the rest in the refrigerator.
- Let it dry for 15 to 20 minutes and then wash it off.
- Practice this twice a day.
TurmericIt is a widely used nutraceutical for its antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties. It reduces redness and inflammation in psoriasis patients by regulating the skin receptors responsible for it.
Garlic
- Apply a few drops of garlic oil directly to the affected area.
- If you have sensitive skin, you can dilute it with a little olive oil.
- You can apply garlic oil twice a day.
GarlicIt is a natural antibiotic.
Aloe vera
- Open the aloe vera leaf and apply the gel inside to the affected area.
- Massage in circular motions for a few minutes.
- Wash off with cold water after 15 minutes.
- Apply the aloe gel three times a day.
Aloe veraIts anti-inflammatory and soothing properties reduce the swelling, itching and redness seen in psoriasis. It also reduces the thickness of the debris and stimulates the growth of fresh cells. It moisturizes and nourishes the skin, making it soft and healthy.
Wheatgrass Juice
- Chop the wheatgrass stalks with a knife and mix them with water in the blender.
- Strain the water using a cloth.
- Add some orange juice or some lemon juice to a quarter cup of wheatgrass juice. Drink this preferably on an empty stomach.
- Store the rest of the wheatgrass juice in the refrigerator.
- Drink it every morning on an empty stomach.
Besides its high chlorophyll content, wheatgrass juice It is rich in vitamins A, B and C and minerals such as magnesium, potassium, sodium, calcium and iron. Drinking wheatgrass juice purifies the blood and neutralizes toxins. It also promotes the growth of new cells.
Green tea
- Soak the green tea bag in hot water for about five minutes.
- Remove the tea bag and drink the tea while it is hot.
- Drink two to three glasses of green tea a day.
Green tea It is known for its antioxidant content. It makes it easier for the body to cope with the disease. Eliminates triggers or toxins that can increase rashes and itching.
saffron tea
- Add 1/4 teaspoon of saffron powder to the cup and pour hot water over it.
- Mix well and wait for it to cool.
- Strain and drink this tea before going to bed.
- You can drink saffron tea every night before going to bed.
Saffron is very useful in skin treatment. It contains antioxidants that cure disease. Its anti-inflammatory properties help reduce swelling and rashes.
Ayran
- Soak 1 cotton ball in buttermilk and apply to the affected areas.
- Wash it off after a few minutes.
- Apply twice a day.
Ayran It soothes inflamed skin and balances the pH of the skin.

Psoriasis Complications
Psoriasis is a troubling ailment on its own. If not managed properly, this skin disorder can cause complications in the functioning of the rest of the body organs.
In some cases, rheumatism may develop due to psoriasis. Rheumatism due to psoriasis can occur in the wrist, fingers, knee, ankle and neck joints. In these cases, there are also skin lesions. People with psoriasis are at higher risk of developing the following conditions;
- Hypertension
- High cholesterol
- Diabetes
- Heart diseases
- Depression